Basic Operating Principles
If you use DHTMLX PHP connectors - please, refer to PHP Connector.
The default package contains an example of the server-side code for PHP (by additional request the similar code for Java/ColdFusion/C#.Net/RubyOnRails can be sent).
In this chapter we'd like to show you dataProcessor in details (a bit changed image from the main page will be to the point).
Let's take a look at the example. You have some data stored in a database and want to represent them in a grid with the possibility to edit them. Let's look inside and learn what role dataProcessor plays here.
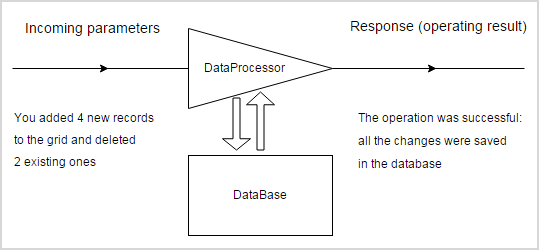
Common request parameters format
First of all, dataProcessor gets the data (all the parameters are part of the GET or POST requests).
The setTransactionMode method is used to set the desired transaction mode.
There are several types of requests:
1) a separate request for each record
dp.setTransactionMode("POST", false);
Request values are:
- id - the record's id
- property1 - 1st data property of an updated record
- property2 - 2nd data property of an updated record
- propertyN - (N+1)th data property of an updated record
- !nativeeditor_status - defines the type of the operation (insert, update, delete), possible values are:
- inserted - the record was added;
- deleted - the record was deleted;
- updated or any other value - the record was updated;
Depending on the value of "!nativeeditor_status" the related section of the server-side logic is triggered.
2) several records in one request
dp.setTransactionMode("POST", true);
Request values are:
- {event1_id}_id - the 1st record's id
- {event1_id}_property1 - 1st data property of the 1st record
- {event1_id}_property2 - 2nd data property of the 1st record
- {event1_id}_propertyN - (N+1)th data property of the 1st record
- {event1_id}_!nativeeditor_status - defines the type of the operation (insert, update, delete), possible values are:
- inserted - the record was added;
- deleted - the record was deleted;
- updated or any other value - the record was updated;
- {event2_id}_id - the 2nd record's id
- {event2_id}_property1 - 1st data property of the 2nd record
- {event2_id}_property2 - 2nd data property of the 2nd record
- {event2_id}_propertyN - (N+1)th data property of the 2nd record
- {event2_id}_!nativeeditor_status - defines the type of the operation (insert, update, delete), possible values are:
- inserted - the record was added;
- deleted - the record was deleted;
- updated or any other value - the record was updated;
- ids - the ids of all the records in the request (ids:{event1_id},{event2_id})
A dataprocessor request can pass any number of data properties. An id is a mandatory parameter, other data properties are completely optional.
3) a request based on the rules of REST API
dp.setTransactionMode("REST");
4) a request sent by dataProcessor in the JSON mode
dp.setTransactionMode("JSON");
Scheduler request params examples
An example of Scheduler request values for a separate request for each record is given below:
- id: 71
- start_date: 2014-11-04 15:00
- end_date: 2014-11-04 18:00
- text: Recinto Ferial - Valencia
- details: Details for Recinto Ferial - Valencia
- !nativeeditor_status: updated
The following example presents Scheduler request values in case of several records in one request:
- 15_id: 15
- 15_start_date: 2015-04-06 10:00
- 15_end_date: 2015-04-06 16:45
- 15_text: New event
- 15_section_id: 3
- 15_!nativeeditor_status:updated
- 16_id: 16
- 16_start_date: 2015-04-08 8:00
- 16_end_date: 2015-04-08 10:00
- 16_text: New event
- 16_section_id: 5
- 16_!nativeeditor_status: updated
- ids: 15,16
Grid and Tree request params
The request values for a grid row update are:
- gr_id - the id of a row in the grid for which some operation is executed;
- !nativeeditor_status - defines the type of the operation (insert, update, delete), possible values are:
- inserted - the row was added;
- deleted - the row was deleted;
- updated or any other value - the row was updated;
- c0 - the data of the first column in the updated row;
- c1 - the data of the second column in the updated row;
- ...
- cN - the data of the (N+1)th column in the grid.
The request values for a tree branch update are:
- tr_id - the id of the node in the tree for which some operation is executed;
- tr_pid - the parent's id;
- tr_order - the node's sequence on the level;
- tr_text - the node's text(label);
- Userdata blocks are passed with their names.
- !nativeeditor_status - the type of the operation, possible values are:
- inserted - item is inserted;
- deleted - item is deleted;
- updated or if an item doesn't exist - item is updated.
Response details
Then dataProcessor processes the incoming parameters, makes all the necessary operations in the database and returns the response.
The response must be a valid XML or JSON in order to be processed correctly.
XML response must have the following format:
<data>
<action type="some" sid="some" tid="some" />
</data>
where:
- type - the type of the operation;
- sid - the original row ID (the same as gr_id);
- tid - the ID of the row after the operation (may be the same as gr_id, or a different one - it can be used during a new row adding, when a temporary ID created on the client-side is replaced with the ID taken from the DB, or by any other business rule).
Since the version 4.1 dataProcessor can work with JSON responses.
A simple JSON response should look as:
{"status":"ok"}
//or
{"tid":121}
A more complex example can be as follows:
{"action":"updated", "sid":15, "tid":15}
To return an error in response of JSON format, use the following code:
{"action":"error", ...}
Types of response
There are 5 predefined types of response:
- updated;
- inserted;
- deleted;
- invalid;
- error.
dataProcessor already contains the logic that defines the default processing of the stated types of response (in other words, actions). You can attach custom handlers to add some extra reaction but, in general, you needn't care about the processing of these actions.
In some cases you may need to return some additional information (the most common use-case - an error during a DB operation). To dispose a problem you can use an additional response type:
function some_error(node)
{
alert(node.getAttribute("type")); // 'my_error'
alert(node.firstChild.data); // Details
return false;
}
dp.defineAction("error",some_error);
where some_error - a custom function which will be called when the response of "my_error" type is received.
<data>
<action type="my_error" sid="id" tid="id">Details</action>
</data>