dhtmlxGantt in Plain JS/HTML
When you develop an application with dhtmlxGantt, the first thing you need is to initialize or, simply speaking, to display the Gantt chart on the page.
This guide tells about initialization of dhtmlxGantt in plain JS and HTML. You can also check the guides on integration with front-end frameworks:
 |  |  |  |
| Angular | React | Svelte | Vue.js |
Creating basic Gantt chart
To display a basic Gantt on the page, follow 3 steps:
- Include the dhtmlxGantt code files on the page.
- Create a DIV container on the page.
- Initialize dhtmlxGantt in the newly created container with the init method. As a parameter the method takes an HTML container (or its id) that the Gantt chart will be displayed in.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="codebase/dhtmlxgantt.js"></script>
<link href="codebase/dhtmlxgantt.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body>
<div id="gantt_here" style='width:1000px; height:400px;'></div>
<script type="text/javascript">
gantt.init("gantt_here");
</script>
</body>
</html>
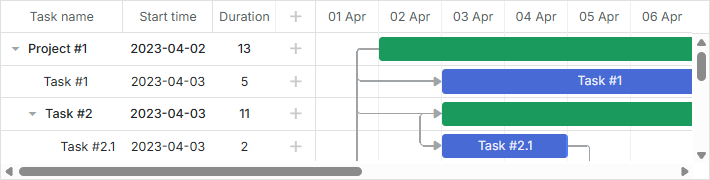
Related sample: Basic initialization
How to add Gantt source files into a project
You can add Gantt code file into your project in several ways, depending on the type of an application you create:
- Include files via the <script> tag
- Import files into ES6/7 and TypeScript apps
- Using Gantt with Vite
- Svelte production build
- Include files into a RequireJS-based app
Include files via the <script> tag
The dhtmlxGantt requires including 2 code files on the page:
- dhtmlxgantt.js
- dhtmlxgantt.css
<script src="codebase/dhtmlxgantt.js"></script>
<link href="codebase/dhtmlxgantt.css" rel="stylesheet">
Let's quickly explore the structure of the dhtmlxGantt package to find out where to look for the files.
Main folders and files that make up the dhtmlxGantt package are:
- sources - the source code files of the library. The files are not minified and easy-to-read. The package is mostly intended to be used for debugging components.
- samples - the code samples
- codebase - the packed code files of the library. These files have much smaller size and intended to be used in production. In your apps you need to use files from this folder
Import files into ES6/7 and TypeScript apps
Use the following command to import files:
import { gantt } from 'dhtmlx-gantt';
For the Commercial, Enterprise or Ultimate version the command look like this:
import { gantt, Gantt } from 'dhtmlx-gantt';
Using Gantt with Vite
If you use Vite in your project, the following setting is required for the vite.config.js file to ensure that Gantt is correctly included into the app:
optimizeDeps: {
include: [
'dhtmlx-gantt',
]
}
Svelte production build
If you use Gantt in a Svelte app, you need to add the following setting into the vite.config.js file for the production build, replacing the gantt_9.0.14_evaluation folder with the path to your Gantt folder:
build: {
commonjsOptions: {
include: [
"node_modules",
"gantt_9.0.14_evaluation/codebase/dhtmlxgantt.js"
]
},
}
Include files into a RequireJS-based app
To include dhtmlxGantt files into a RequireJS-based app, you need to follow the logic shown in the example below:
requirejs(["codebase/dhtmlxgantt"], (dhx) => {
const gantt = dhx.gantt;
const Gantt = dhx.Gantt; // for Enterprise builds
gantt.init("gantt_here");
gantt.parse({
tasks: [
{ id: 1, text: "Project #2", start_date: "01-04-2025", duration: 18, progress: 0.4, open: true },
{ id: 2, text: "Task #1", start_date: "02-04-2025", duration: 8, progress: 0.6, parent: 1 },
{ id: 3, text: "Task #2", start_date: "11-04-2025", duration: 8, progress: 0.6, parent: 1 }
],
links: [
{ id: 1, source: 1, target: 2, type: "1" },
{ id: 2, source: 2, target: 3, type: "0" }
]
});
});
The dhtmlxGantt library will return an object with fields gantt and Gantt (in Commercial, Enterprise or Ultimate versions) - the gantt and Gantt objects described here.
When using Gantt with custom extensions in RequireJS, you should specify the shim config for RequireJS and directly set the dependency of extensions from Gantt in it.
The example below demonstrates how a custom extension file custom_tooltip_plugin.js can be set in the correct way:
requirejs.config({
paths: {
"dhtmlxgantt": "../../codebase/dhtmlxgantt",
"ext/dhtmlxgantt_custom_tooltip": "../custom_tooltip_plugin"
},
shim: {
"ext/dhtmlxgantt_custom_tooltip": ["dhtmlxgantt"]
}
});
requirejs(["dhtmlxgantt"], (dhx) => {
const gantt = dhx.gantt;
const date_to_str = gantt.date.date_to_str(gantt.config.task_date);
const today = new Date();
gantt.addMarker({
start_date: today,
css: "today",
text: "Today",
title: `Today: ${date_to_str(today)}`
});
gantt.init("gantt_here");
gantt.parse({
tasks: [
{ id: 1, text: "Project #2", start_date: "01-04-2025", duration: 18, progress: 0.4, open: true },
{ id: 2, text: "Task #1", start_date: "02-04-2025", duration: 8, progress: 0.6, parent: 1 },
{ id: 3, text: "Task #2", start_date: "11-04-2025", duration: 8, progress: 0.6, parent: 1 }
],
links: [
{ id: 1, source: 1, target: 2, type: "1" },
{ id: 2, source: 2, target: 3, type: "0" }
]
});
});
Check that the module name for any file inside the package is specified as a relative path inside the 'codebase' folder of the package plus the filename, for instance:
core library:
- "dhtmlxgantt": "./vendor/dhtmlxgantt/dhtmlxgantt"
Full screen mode
To correctly display a Gantt chart in the full-screen mode in different browsers, define the following style on the page:
<style type="text/css" media="screen">
html, body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
height: 100%;
overflow: hidden;
}
</style>