Integrating Vault with Svelte
You should be familiar with the basic concepts and patterns of Svelte to use this documentation. If you are not, please refer to the Svelte documentation for a getting-started tutorial.
DHTMLX Vault is compatible with Svelte. You can check the corresponding example on GitHub: DHTMLX Vault with Svelte Demo.
Creating a project
To create a Svelte project we will use Svelte with Vite and run the following command:
npm create vite@latestCheck the details in the related article.
Installation of dependencies
Independent of the chosen way, next you should go to the app directory. Let's call our project vault-svelte and run:
cd vault-svelteThen you need to install dependencies and run the app. For this, you need to make use of a package manager:
- if you use yarn, you need to call the following commands:
yarn install
yarn dev
- if you use npm, you need to call the following commands:
npm install
npm run dev
When the above steps are complete, your app should be running on http://localhost:5173.

Creating Vault
Now we should get the DHTMLX Vault code. First of all, we need to stop the app by pressing Ctrl+C in the command line. Then we can proceed with installing the Vault package.
Step 1. Package installation
There are two options available: you can install the Pro package from a local folder or install the trial version using npm or yarn.
Installing the package from a local folder
The instructions are the following:
- Copy the Vault package into some local directory inside the project
- In the project directory run the command below replacing vault-local-package-path with the actual path:
npm install ./vault-local-package-path
//or
yarn add "./vault-local-package-path"
For example:
npm install ./vault_5.0.0_enterprise
// or
yarn add "./vault_5.0.0_enterprise"
Installing the trial version via a package manager
You can install the trial version of Vault using npm or yarn commands:
- for npm:
npm config set @dhx:registry https://npm.dhtmlx.com
npm i @dhx/trial-vault
- for yarn:
yarn config set @dhx:registry https://npm.dhtmlx.com
yarn add @dhx/trial-vault
To get Vault under the proprietary license, refer to the Support Center!
Step 2. Component creation
Now we should create a Svelte component, to add a Vault into the application. Let's create a new file in the src/ directory and name it Vault.svelte.
Importing source files
Open the file and import Vault source files. Note that:
- if you've installed the Vault package from a local folder, your import paths will look like this:
Vault.svelte
import { Vault } from 'dhx-vault-package';
import 'dhx-vault-package/codebase/vault.css';
Note that depending on the used package, the source files can be minified. In this case make sure that you are importing the CSS file as vault.min.css.
In case you use npm with a local Vault package, the way of importing Vault source files is different. Check the details below
- if you've chosen to install the trial version, the import paths should be as in:
Vault.svelte
import { Vault } from '@dhx/trial-vault';
import '@dhx/trial-vault/codebase/vault.min.css';
In this tutorial we will use the trial version of Vault.
Setting the container and adding Vault
To display Vault on the page, we need to set the container to render the component inside. Check the code below:
Vault.svelte
<script> import { Vault } from "@dhx/trial-vault";
import "@dhx/trial-vault/codebase/vault.min.css";
let container;
</script>
<div bind:this={container} class="container"></div>
<style> .container {
width: 440px;
height: 400px;
margin: 50px auto;
}
</style>
Then we need to render our Vault in the container. To do that, use the onMount() method of Svelte. Inside the method you can also specify the destructor() method to remove the Vault instance, when it is no longer needed:
Vault.svelte
<script> import { Vault } from "@dhx/trial-vault";
import "@dhx/trial-vault/codebase/vault.min.css";
import { onMount } from "svelte";
let container;
let vault;
onMount(() => { vault = new Vault(container,{}); return () => vault.destructor(); });
</script>
<div bind:this={container}></div>
In case you use npm with a local Vault package, the way of Vault initialization differs a little bit. Check the details below
Using npm + Vault package
If you use npm with a Vault package, the import of the source files and the initialization of Vault will differ from the common way:
- include the Vault source files in the index.html file as shown in the example below. Replace vault_package with the name of your local folder that contains Vault source files:
index.html
<script src="./vault_package/codebase/vault.min.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./vault_package/codebase/vault.min.css">
- use the dhx prefix to initialize Vault, check the example below:
Vault.svelte
<script> import { onMount } from "svelte";
let container;
let vault;
onMount(() => {
vault = new dhx.Vault(container, {}); });
</script>
Loading data
To add data into the Vault, we need to provide a data set. Let's create the data.js file in the src/ directory and add some data into it:
data.js
export function getData() {
return [
{
size: "100000",
name: "index.php",
},
{
size: "25555",
name: "index.js",
},
{
size: "2555412",
name: "document.doc",
},
{
size: "52555",
name: "documentation.pdf",
},
{
size: "23555",
name: "archive.zip",
},
{
size: "72555",
name: "prototype.psd",
},
];
}
Then open the Vault.svelte file, specify the line for data export and use the parse() method to load data:
Vault.svelte
<script> import { Vault } from "@dhx/trial-vault";
import "@dhx/trial-vault/codebase/vault.min.css";
import { onMount } from "svelte";
export let data;
let vault;
let container;
onMount(() => {
vault = new Vault(container, {});
});
$: vault?.data.parse(data);
</script>
<div bind:this={container}></div>
The $: vault?.data.parse(data); line will provide data reloading on each applied change.
Now the Vault component is ready. When the element will be added to the page, it will initialize the Vault object with data. You can provide necessary configuration settings as well. Visit our Vault API docs to check the full list of available properties.
Handling events
When a user makes some action in the Vault, it invokes an event. You can use these events to detect the action and run the desired code for it. See the full list of events.
Open Vault.svelte and complete the onMount() method as in:
Vault.svelte
onMount(() => {
vault = new Vault(container, {});
vault.events.on("ActionName", () => {do something});
});
Replace 'ActionName' with the actual name of the event you want to handle, and implement the corresponding code inside the callback function. Get more information about the work with events in the Handling Events article.
Step 3. Adding Vault into the app
Now it's time to add the component into our app. Open App.svelte and replace the default code with the following one:
App.svelte
<script> import Vault from "./Vault.svelte";
import { getData } from "./data.js";
</script>
<Vault data={getData()} />
After that, when we start the app, we should see Vault loaded with data on a page.
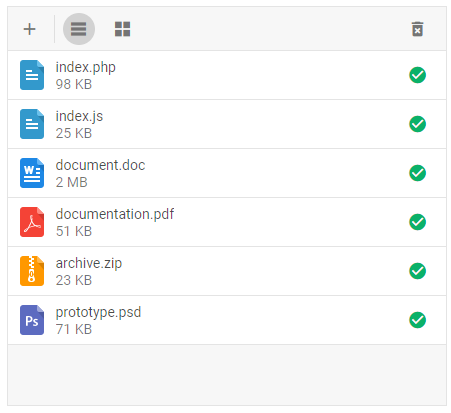
Now you should have a basic setup for integrating DHTMLX Vault with Svelte. You can customize the code according to your specific requirements.
Back to top