Integration with Vue
It's helpful to know the basics of Vue before diving into this guide. If you need a refresher, check out the Vue 3 documentation.
DHTMLX Kanban works smoothly with Vue. There are sample code snippets demonstrating how to use DHTMLX Kanban with Vue 3. For more details, see the Example on GitHub.
Creating a project
Make sure Node.js is installed before starting a new project.
To spin up a Vue project, just use:
npm create vue@latest
This command sets up and runs create-vue, which is the official Vue project starter. For more info, take a look at the Vue.js Quick Start.
In this example, the project is named my-vue-kanban-app.
Installation of dependencies
Move into your app’s folder:
cd my-vue-kanban-app
Install the dependencies and start up the development server. Depending on your package manager, use one of these:
- For yarn:
yarn
yarn start // or yarn dev
- For npm:
npm install
npm run dev
The app should now be running locally (for example, at http://localhost:3000).
Creating Kanban
Next, grab the DHTMLX Kanban source code. Stop the app for now, and install the Kanban package.
Step 1. Package installation
Download the trial Kanban package and follow the steps in the README. The trial version is available for 30 days.
Step 2. Component creation
Create a new Vue component to add Kanban with a Toolbar to your app. In the src/components/ directory, make a new file called Kanban.vue.
Import source files
Open Kanban.vue and import the Kanban source files. Keep in mind:
- If you’re using the PRO version and installed the Kanban package from a local folder, your imports will look like this:
<script>
import { Kanban, Toolbar } from 'dhx-kanban-package';
import 'dhx-kanban-package/dist/kanban.css';
</script>
Depending on your package, the source files might be minified. In that case, make sure to import kanban.min.css instead.
- If you’re using the trial version, use these paths:
<script>
import { Kanban, Toolbar } from '@dhx/trial-kanban';
import '@dhx/trial-kanban/dist/kanban.css';
</script>
This guide shows how to set up the trial version of Kanban.
Setting containers and adding Kanban with Toolbar
To show Kanban with a Toolbar, set up containers for both and initialize them with their constructors:
<script>
import { Kanban, Toolbar } from "@dhx/trial-kanban";
import "@dhx/trial-kanban/dist/kanban.css";
export default {
mounted() {
// initialize the Kanban component
this.kanban = new Kanban(this.$refs.kanban_container, {});
// initialize the Toolbar component
this.toolbar = new Toolbar(this.$refs.toolbar_container, {
api: this.kanban.api, // provide Kanban inner API
// other configuration properties
});
},
unmounted() {
this.kanban.destructor(); // destruct Kanban
this.toolbar.destructor(); // destruct Toolbar
}
};
</script>
<template>
<div class="component_container">
<div ref="toolbar_container"></div>
<div ref="kanban_container" class="widget"></div>
</div>
</template>
Adding styles
To make Kanban display properly, add these styles to your main CSS file:
/* specify styles for initial page */
html,
body,
#app { /* make sure that you use the #app root container */
height: 100%;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
/* specify styles for Kanban and Toolbar container */
.component_container {
height: 100%;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* specify styles for Kanban container */
.widget {
height: calc(100% - 56px);
}
Loading data
To provide data for Kanban, create a data.js file in the src/ directory and add your data like this:
export function getData() {
const columns = [
{
label: "Backlog",
id: "backlog"
},
{
label: "In progress",
id: "inprogress"
},
// ...
];
const cards = [
{
id: 1,
label: "Integration with Angular/React",
priority: 1,
color: "#65D3B3",
start_date: new Date("01/07/2021"),
users: [3, 2],
column: "backlog",
type: "feature",
},
{
label: "Archive the cards/kanbans ",
priority: 3,
color: "#58C3FE",
users: [4],
progress: 1,
column: "backlog",
type: "feature",
},
// ...
];
const rows = [
{
label: "Feature",
id: "feature",
},
{
label: "Task",
id: "task",
}
];
return { columns, cards, rows };
}
Now, open App.vue, import the data, and set it up using the data() method. Then pass it to the <Kanban/> component as props:
<script>
import Kanban from "./components/Kanban.vue";
import { getData } from "./data";
export default {
components: { Kanban },
data() {
const { columns, cards, rows } = getData();
return {
columns,
cards,
rows
};
}
};
</script>
<template>
<Kanban :columns="columns" :cards="cards" :rows="rows"/>
</template>
Then, in Kanban.vue, use these props in the Kanban configuration object:
<script>
import { Kanban, Toolbar } from "@dhx/trial-kanban";
import "@dhx/trial-kanban/dist/kanban.css";
export default {
props: ["cards", "columns", "rows"],
mounted() {
this.kanban = new Kanban(this.$refs.kanban_container, {
cards: this.cards,
columns: this.columns,
rows: this.rows,
rowKey: "type",
// other configuration properties
});
this.toolbar = new Toolbar(this.$refs.toolbar_container, {
api: this.kanban.api,
// other configuration properties
});
},
unmounted() {
this.kanban.destructor();
this.toolbar.destructor();
}
};
</script>
<template>
<div class="component_container">
<div ref="toolbar_container"></div>
<div ref="kanban_container" class="widget"></div>
</div>
</template>
Alternatively, you can use the setConfig() or parse() method in the mounted() hook to load data into Kanban:
<script>
import { Kanban, Toolbar } from "@dhx/trial-kanban";
import "@dhx/trial-kanban/dist/kanban.css";
export default {
props: ["cards", "columns", "rows"],
mounted() {
this.kanban = new Kanban(this.$refs.kanban_container, {
columns: [],
cards: [],
rows: [],
rowKey: "type",
// other configuration properties
});
this.toolbar = new Toolbar(this.$refs.toolbar_container, {
api: this.kanban.api,
// other configuration properties
});
this.kanban.setConfig({
cards: this.cards,
columns: this.columns,
rows: this.rows
});
},
unmounted() {
this.kanban.destructor();
this.toolbar.destructor();
}
};
</script>
<template>
<div class="component_container">
<div ref="toolbar_container"></div>
<div ref="kanban_container" class="widget"></div>
</div>
</template>
The setConfig or parse() method lets you reload data whenever changes are made.
At this point, the Kanban component is set up and ready. Once you add it to the page, it initializes with your data. You can also pass in any extra configuration you need. To see all available properties, visit the Kanban API docs.
Handling events
When actions happen in Kanban, events are triggered. You can listen for these events and run your own code in response. Check out the full list of events.
In Kanban.vue, update the mounted() method like this:
<script>
// ...
export default {
// ...
mounted() {
this.kanban = new Kanban(this.$refs.cont, {});
this.kanban.api.on("add-card", (obj) => {
console.log(obj.columnId);
});
},
unmounted() {
this.kanban.destructor();
}
}
</script>
// ...
Now, go ahead and run the app to see the Kanban board loaded with your data.
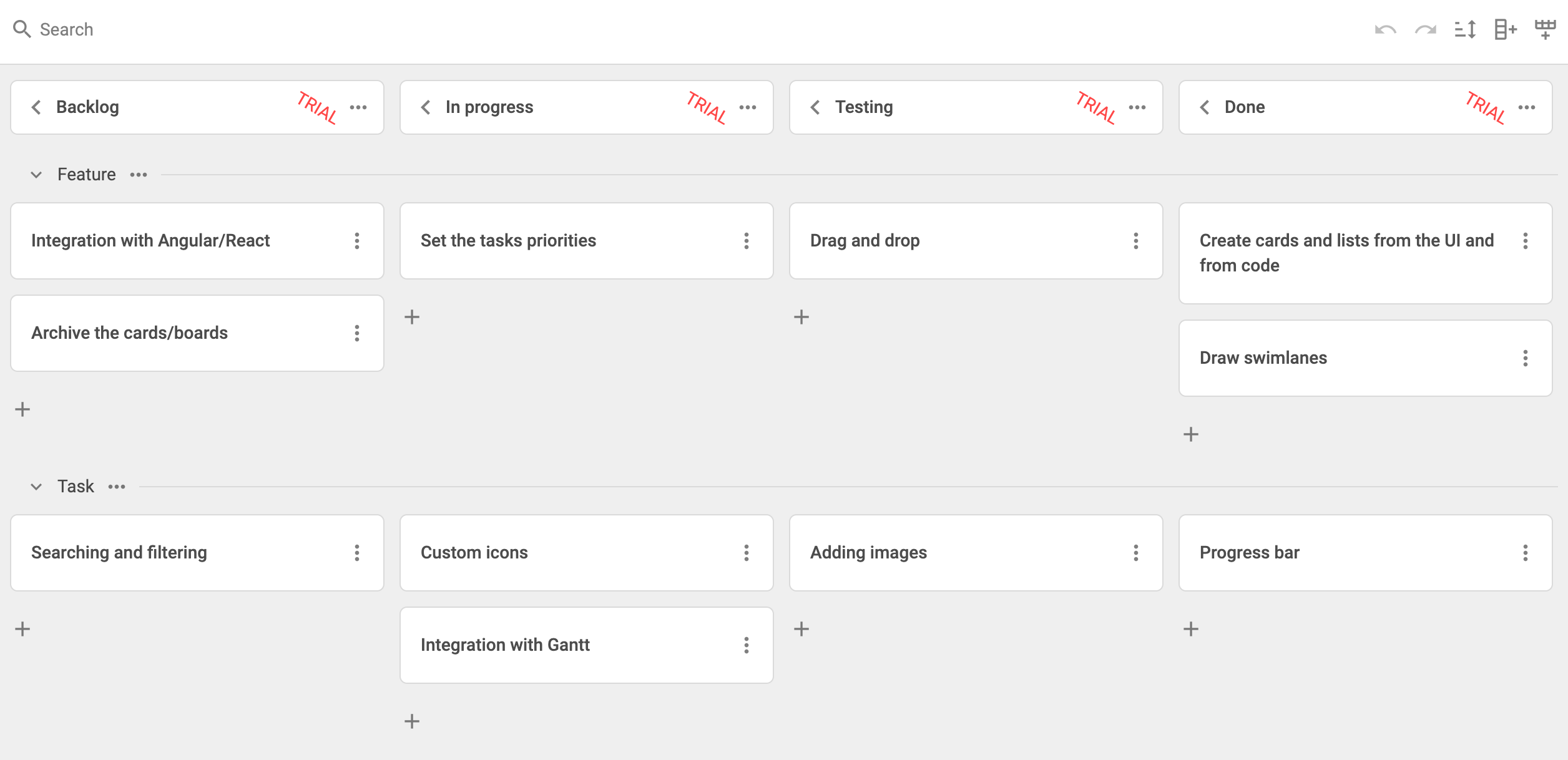
This is the basic setup for integrating DHTMLX Kanban with Vue. The code can be tweaked as needed. For a more advanced example, check out the project on GitHub.